Current Success Stories
Materials for Additive Manufacturing
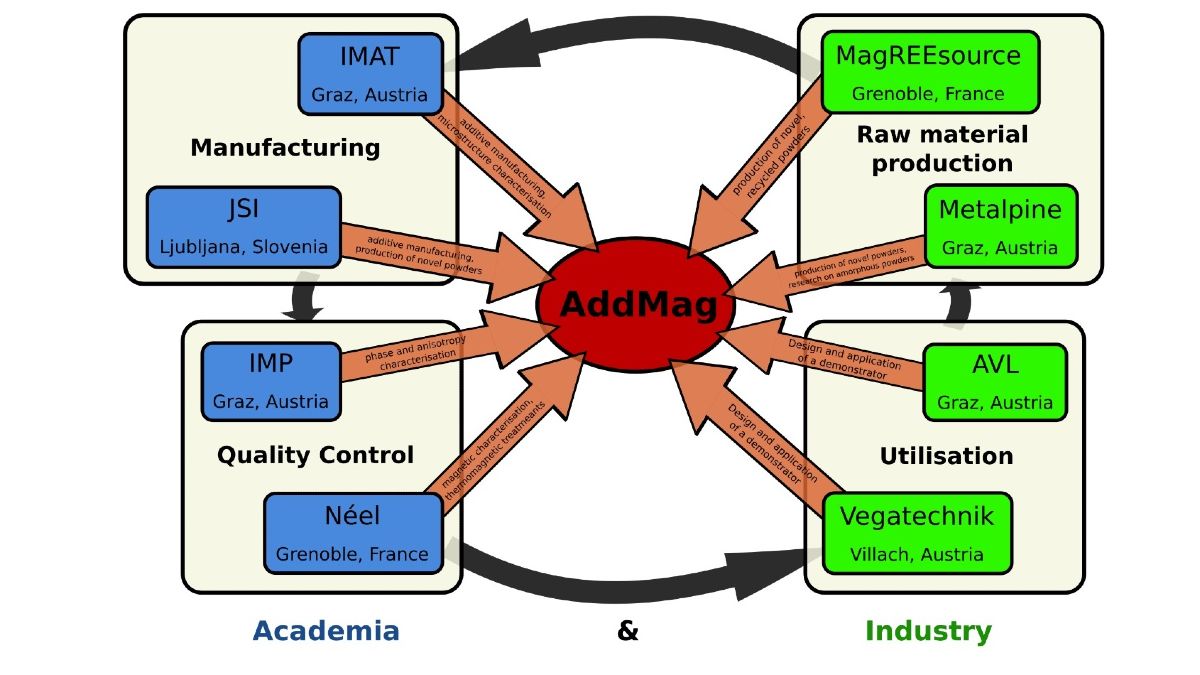
AddMag
The AddMag project has successfully demonstrated that additive manufacturing (AM) can produce permanent magnets with exceptional magnetic performance, dimensional accuracy, and sustainability. At the heart of the project was the ambition to replace conventional, inflexible manufacturing processes with AM, which enables near-net-shape production and reduces reliance on virgin rare earth materials.

Materials for Additive Manufacturing
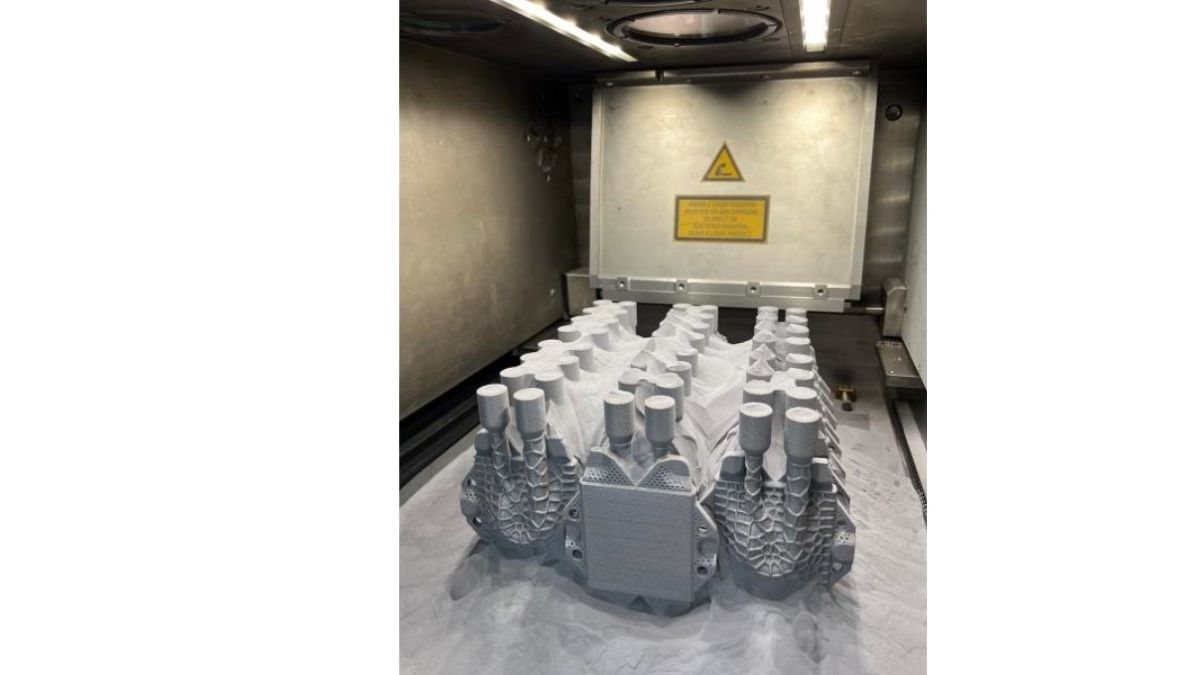
AM2pC
The AM2pC project successfully demonstrated a new class of additively manufactured (AM) two-phase cooling systems capable of handling extreme heat loads relevant for next-generation AI and high-performance computing (HPC) infrastructure.
Materials for Additive Manufacturing
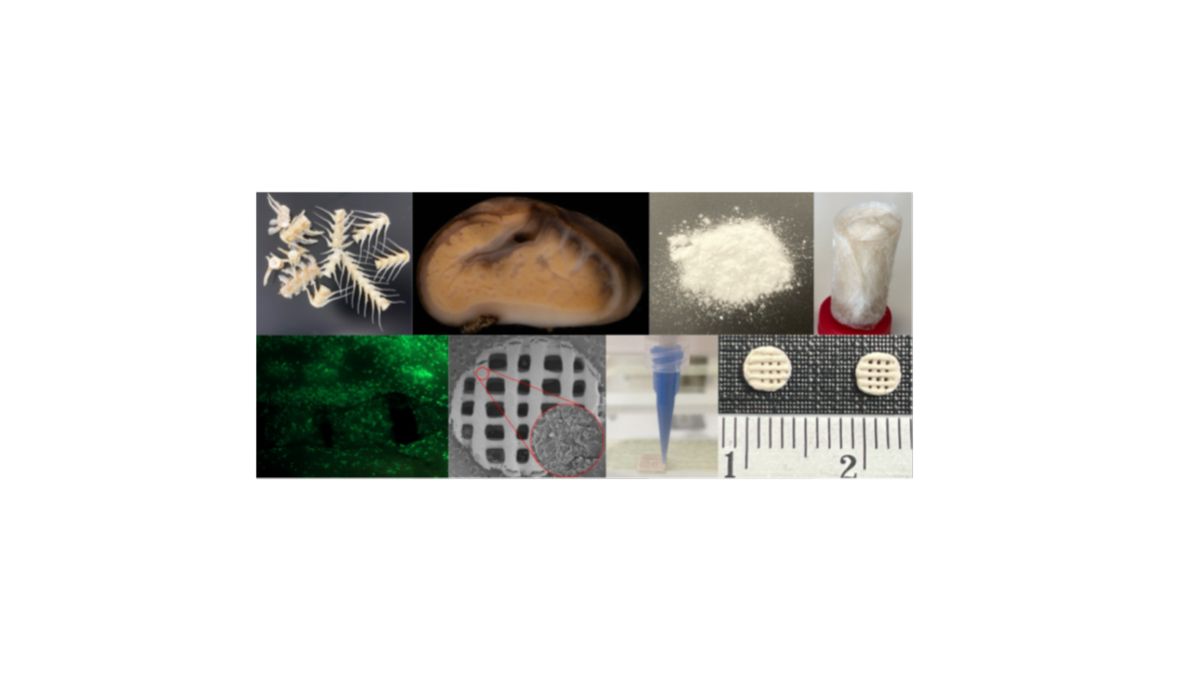
BiogenInk
Although 3D printing is arising as a versatile and potent technology for production of biomaterials, in particular tissue engineering (TE) scaffolds, its maturation is still hampered by the limited materials that can be used. BiogenInk project addressed this scientific challenge by aiming the development of bioinspired and bioresorbable inks composed of marine collagen and ionic-doped calcium phosphates, as building blocks for the production of cell instructive scaffolds for bone regeneration. .
(Multi)Functional materials
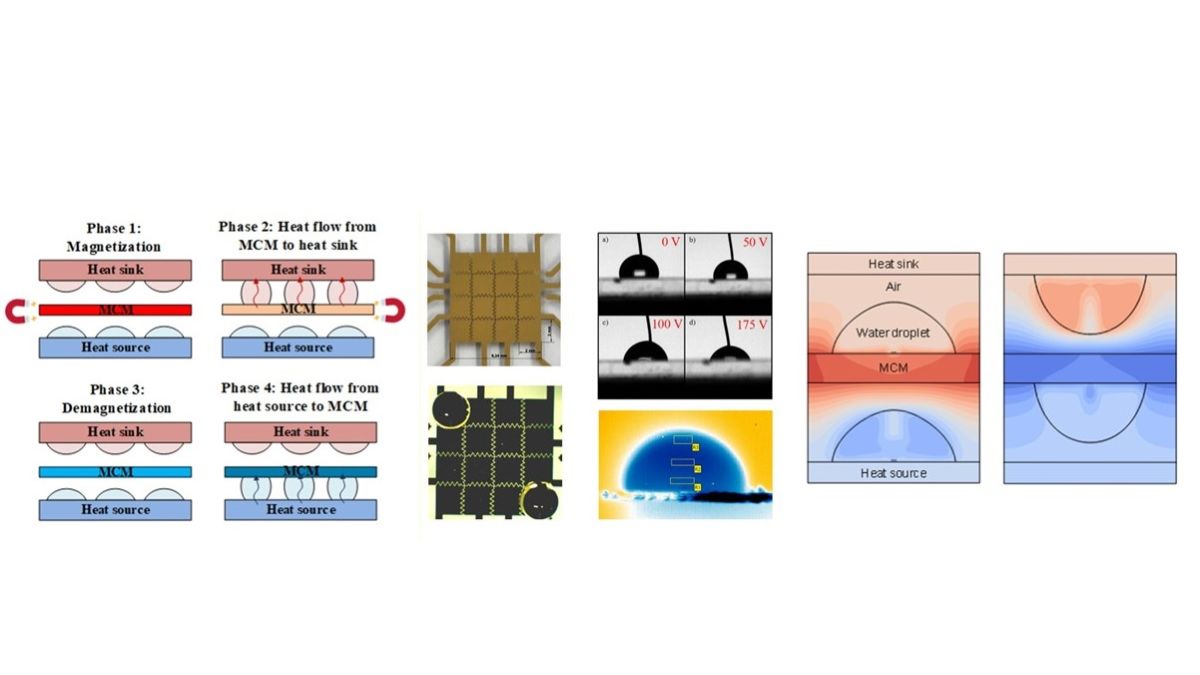
Cool BatMan
The aim of the Cool BatMan project was to establish a fundamental understanding of the dynamic thermal behavior of two physical phenomena coupled within a compact magnetocaloric cooling device. A magnetocaloric material (and the associated magnetocaloric effect) was combined with the phenomenon of electrowetting-on-dielectric (digital microfluidics), resulting in a unique magnetocaloric cooling concept that could in the future serve as a BTMS for batteries in e-mobility.
Materials for additive manufacturing
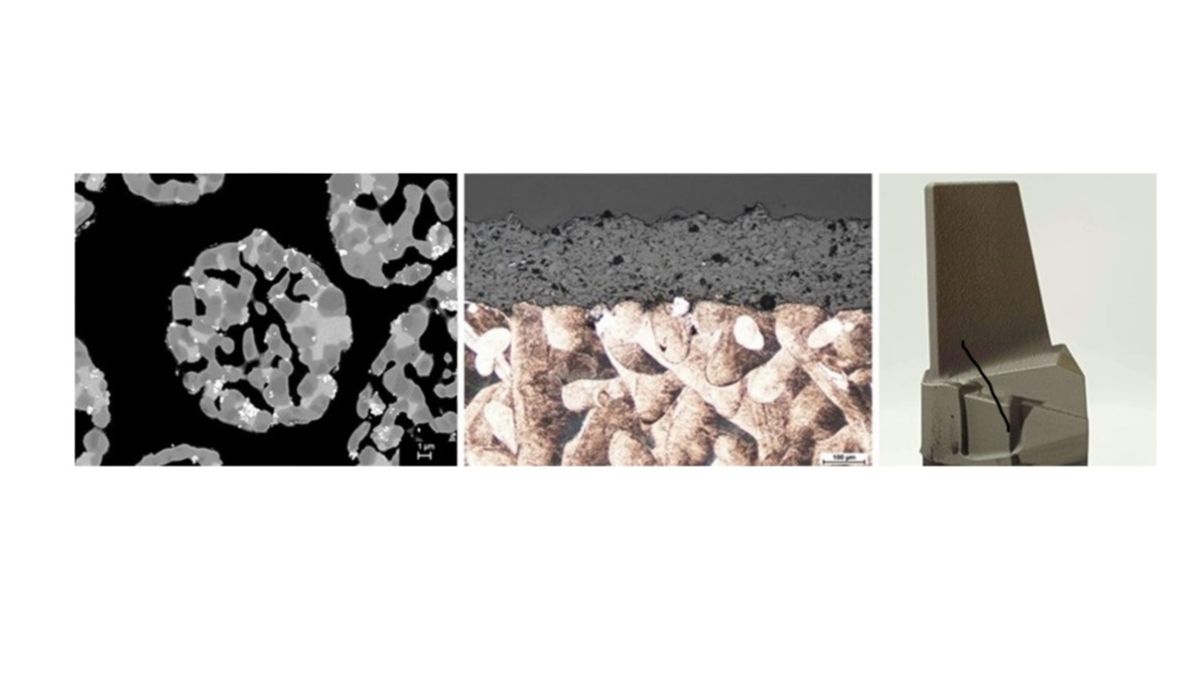
DePriSS
The DePriSS project focused on combining advanced 3D printing and thermal spraying technologies to develop components with improved wear and fatigue resistance under dynamic and cyclic loads. By integrating these two additive manufacturing methods, the project aimed to overcome traditional manufacturing limitations and achieve superior surface properties for high-tech applications. Within the project duration, several specific achievements were reached.

High Performance Composites / Biobased Performance Material
DURACER
The DURACER project developed ceramic tool composites based on alumina reinforced with super-hard cubic boron nitride (cBN) particles. The composites, in accordance with the project assumptions, were obtained using the Spark Plasma Sintering method. The main challenge was the metastability of cBN under SPS conditions. At high temperatures, cBN transforms into a hexagonal, graphite-like form and therefore ultra-high pressure must also be ensured during its sintering to avoid cBN-->hBN transition.
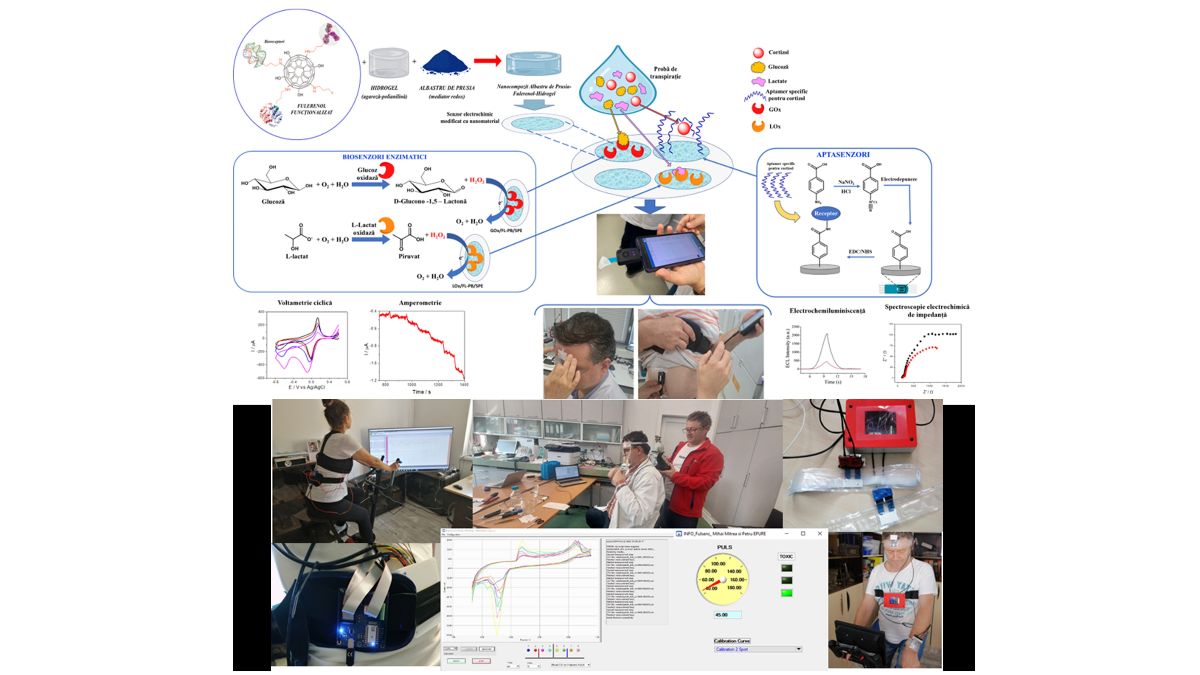
Multifunctional materials
FULSENS-GEL
The M-ERA.NET FULSENS-GEL project aimed to develop an innovative nanocomposite material, based on the combination of elastic, resistant and flexible hydrogels with functionalized Fullerenol (FL)-based nanomaterials, thus obtaining new conductive hydrogels, with tunable network structures, active surface and improved electrochemical, mechanical and optical properties.

High performance composites
GRADIENT
The project’s objective was therefore to develop new methodologies and validation tools for interphase optimization, while also exploring approaches to reduce stress concentrations within the interphase to enhance the durability of composite structures.

Multifunctional materials
GEOSUMAT
The GEOSUMAT project has the objective of utilizing local waste materials as replacements for all compounds in geopolymers, namely precursors, activators, and aggregates. Over 30 different materials were analyzed using various techniques such as Xray fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, etc., and classified as geopolymer input materials in the developed database.
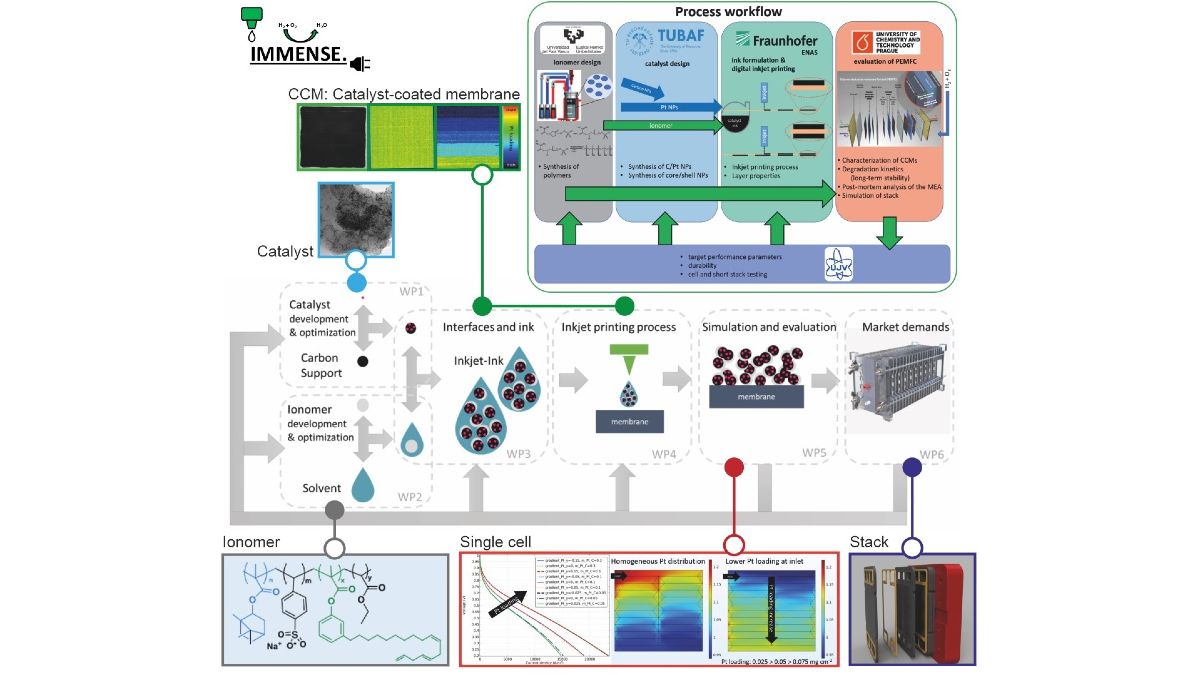
Multifunctional materials
IMMENSE
In the course of global undertakings to achieve a CO2-neutral energy economy, the German-Spanish-Czech consortium of the project named IMMENSE targets the UN sustainable development goals (SDG) 7 and 9. In detail, it plans to make impact on the current fuel cell technology by tailoring the catalytic ink and processing it using digital inkjet-printing technology supplementing the currently used analogous processes.
Multifunctional materials
KESPER
The project ventured into developing multinary kesterite compound for photoelectrochemical water splitting and ammonia generation. Despite relentless efforts to improve, the instability of kesterite in aqueous media and control over phase impurities posed a setback to achieve the ambitious objectives of the project.
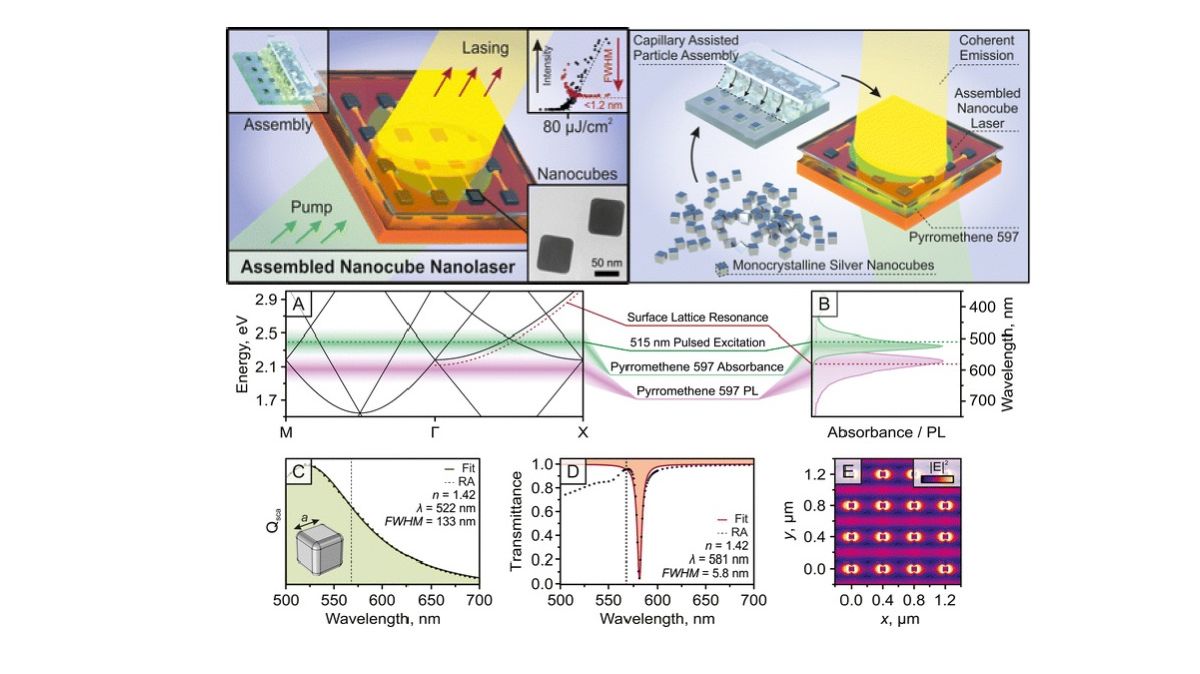
Multifunctional materials
LaSensA
Our study on nanolasers performed within a project by partners Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania and National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), Japan, has achieved significant international acclaim. The research, detailed in the article "Lasing in an assembled array of silver nanocubes" published in Nanoscale Horizons, introduces a novel approach to developing plasmonic nanolasers.
New strategies for advanced material-based technologies for health applications
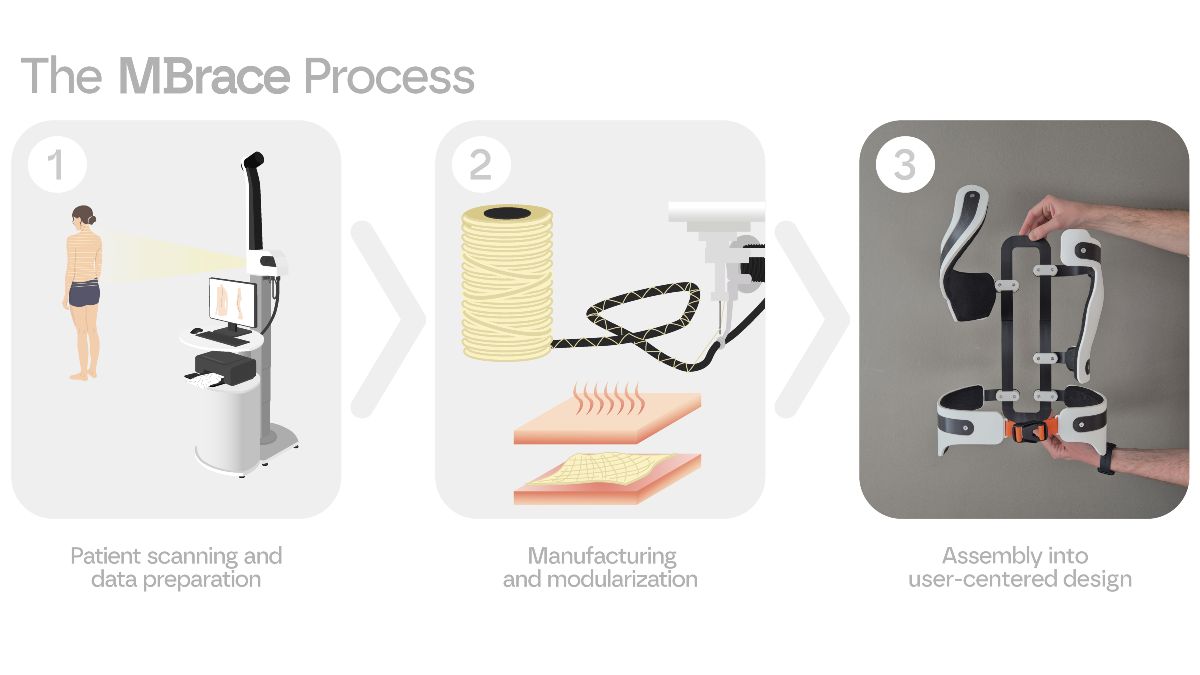
MBrace
Every year, 22 million Europeans are treated for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, a spinal deformation developing during the ages ten to eighteen. The MBrace project aimed to significantly improve the well-being of these young patients. It combined innovative developments of functional multi-matrix composites, high-strength mineral fibers, cost-efficient manufacturing and non-invasive AI-based monitoring with fashionable design to develop the lightest possible brace.

Multifunctional materials
NanoElMem
The NanoElMem project presents an innovative approach towards the design and fabrication of materials for the creation of direct alkaline ethanol fuel cells (DAEFC). Emphasis was put on the development of platinum (Pt)-free anode catalysts and nano-composite membranes, where environmentally friendly and sustainable polysaccharides and inorganic materials were employed.
Materials for Health Applications
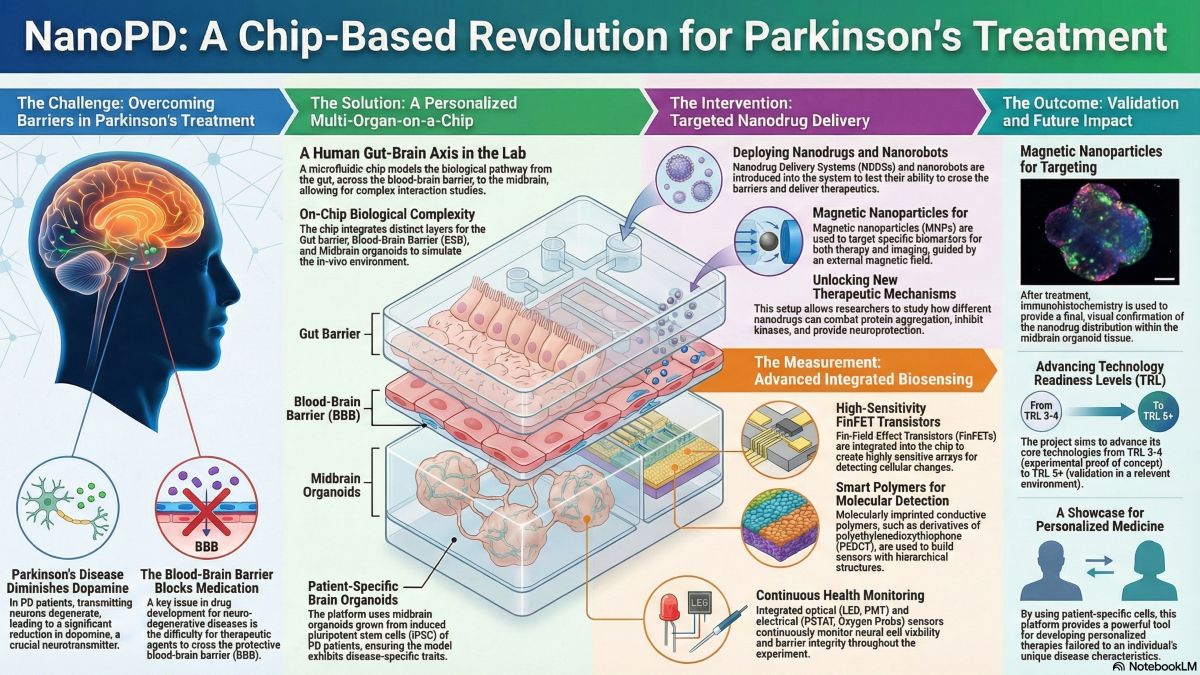
nanoPD
The nanoPD project focuses on modeling biological barriers in vitro using multi-compartment microfluidic chips containing human midbrain organoids to develop new theranostics for Parkinson's Disease (PD). These organoids, derived from PD patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), exhibit neurodegeneration phenotypes, allowing for personalized disease modeling.

Multifunctional materials
NanOx4Estor
The NanOx4EStor project (Nanoscaled Ferroelectric (Pseudo)-Binary Oxide Thin Film Supercapacitors for Flexible and Ultrafast Pulsed Power Electronics) aims to develop innovative, cost-effective, high-throughput methods for fabricating advanced dielectric capacitors.

Materials for Health Applications
Nano4Glio
Nano4Glio aims to develop an innovative implantable device for the continuous and targeted treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. This biodegradable device is designed to co-deliver the gold-standard drug (temozolomide) and a MGMT protein inhibitor directly to brain tumor cells, overcoming the limitations of current GBM therapies, such as low drug bioavailability and resistance mechanisms. By enhancing drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier and enabling localized, sustained release, Nano4Glio seeks to improve therapeutic outcomes and reduce side effects for GBM patients.
Innovative Surfaces, Coatings and Interfaces
SLIM-FIT
Main objective of "SLIM-FIT" is to establish an advanced battery cell design based on innovative, interpenetrating electrode and separator coatings aiming for stable and safe Lithium-Sulfur (Li-S) batteries for mobile applications. The concept uses a widely un-explored regime of "slim" electrode dimensions (10 µm – 20 µm thickness compared to 80 µm - 100 µm in state-of-the-art battery cells), specifically "fitted" to the requirements of high performance Li-S technology. Aim is to demonstrate the new concept in prototype Lithium-Sulfur battery cells in an application-relevant evaluation.
Multifunctional materials
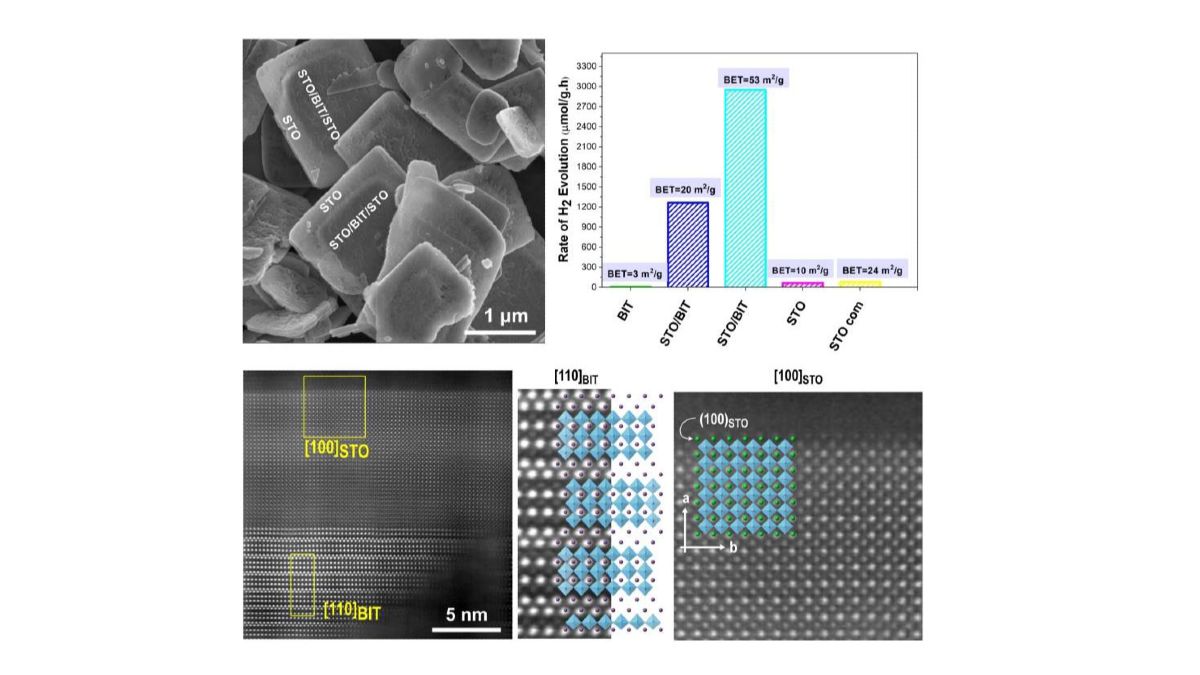
SunToChem
The main aim of the SunToChem project was to design new efficient H2-evolution photocatalysts. The engineering of the photocatalysts was performed based on an in-depth understanding of nucleation-crystallization phenomena and supported by density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The research was focused on perovskite titanates, particularly on two-dimensional (2D) SrTiO3/Bi4Ti3O12 nanoheterostructures, 2D SrTiO3 nanoplatelets, SrTiO3 cube-like particles with different types of exposed facets and Al-doped SrTiO3 particles.
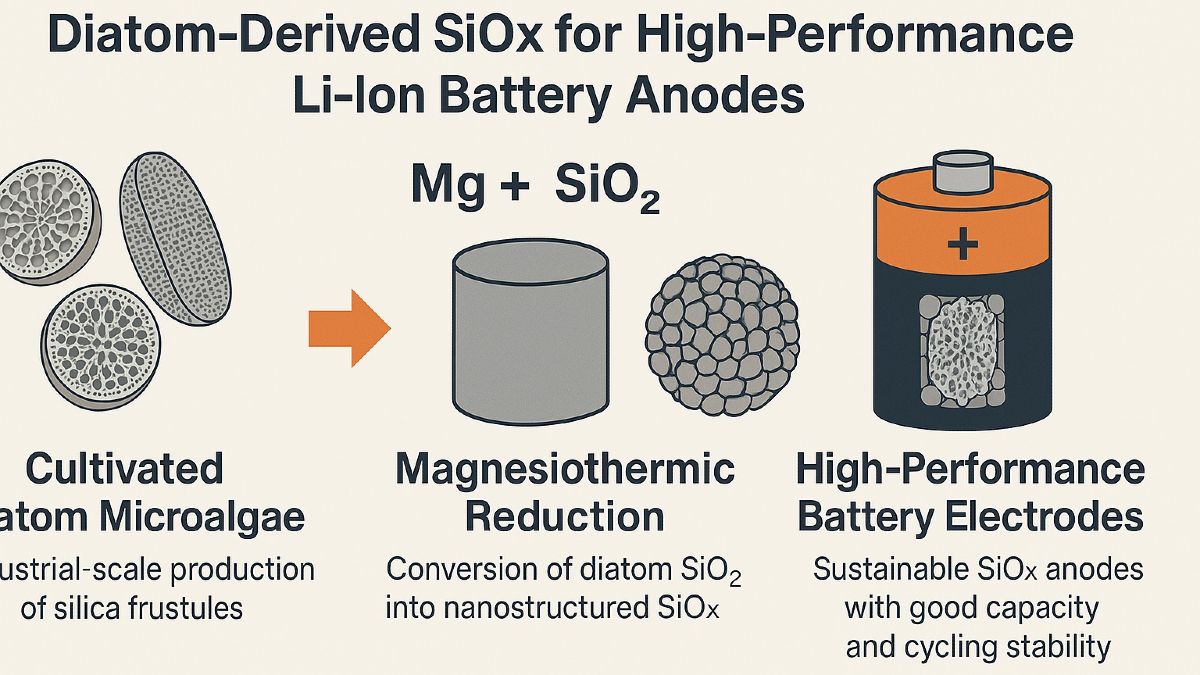
Multifunctional materials
SUSTBATT
This project has been highly successful in establishing new scientific and technological foundations for the use of biologically derived silica in energy storage applications. Our work demonstrated, for the first time, that industrially cultivated diatom microalgae can be effectively employed as a renewable template for the synthesis of nanostructured silicon suboxide (SiOx) materials, which are promising negative electrodes for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs).
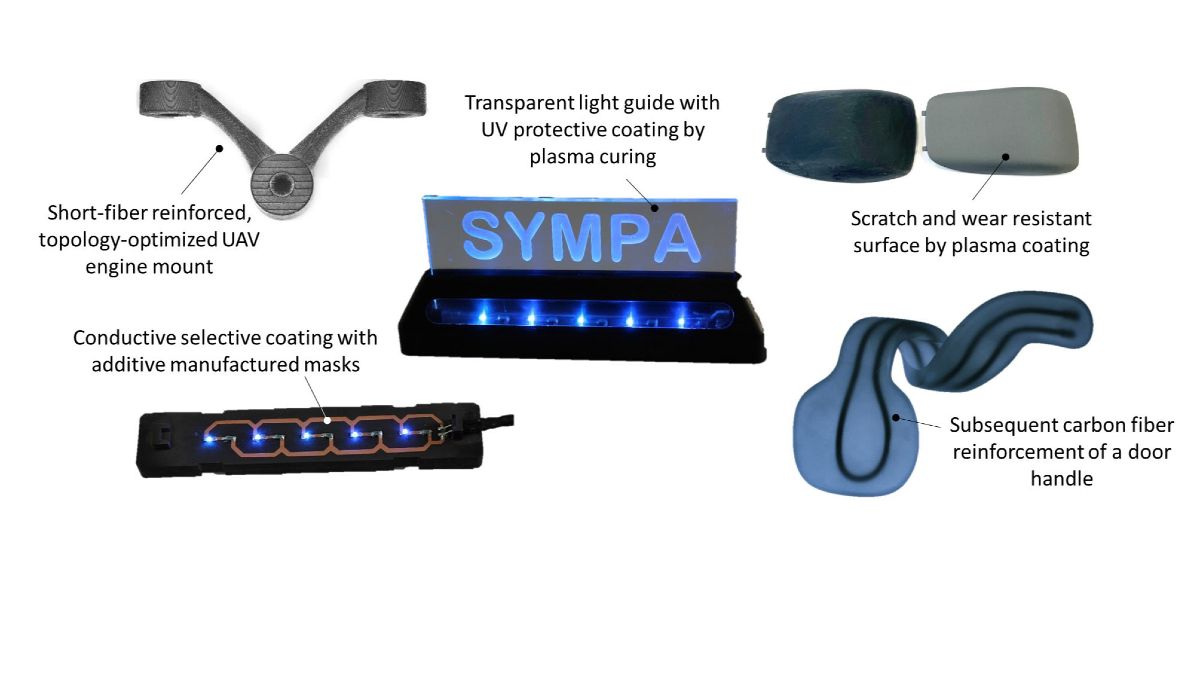
Materials for Additive Manufacturing
SYMPA
Stereolithography is an additive manufacturing method, which enables high-precision processing of thermoset resins, mostly acrylate- or epoxy-based photopolymers. Material consumption is comparable low because the unused resins can be re-used and even transparent components can be manufactured. However, mechanical properties and long-term stability of such components are rather low, hindering their use for durable automotive applications.
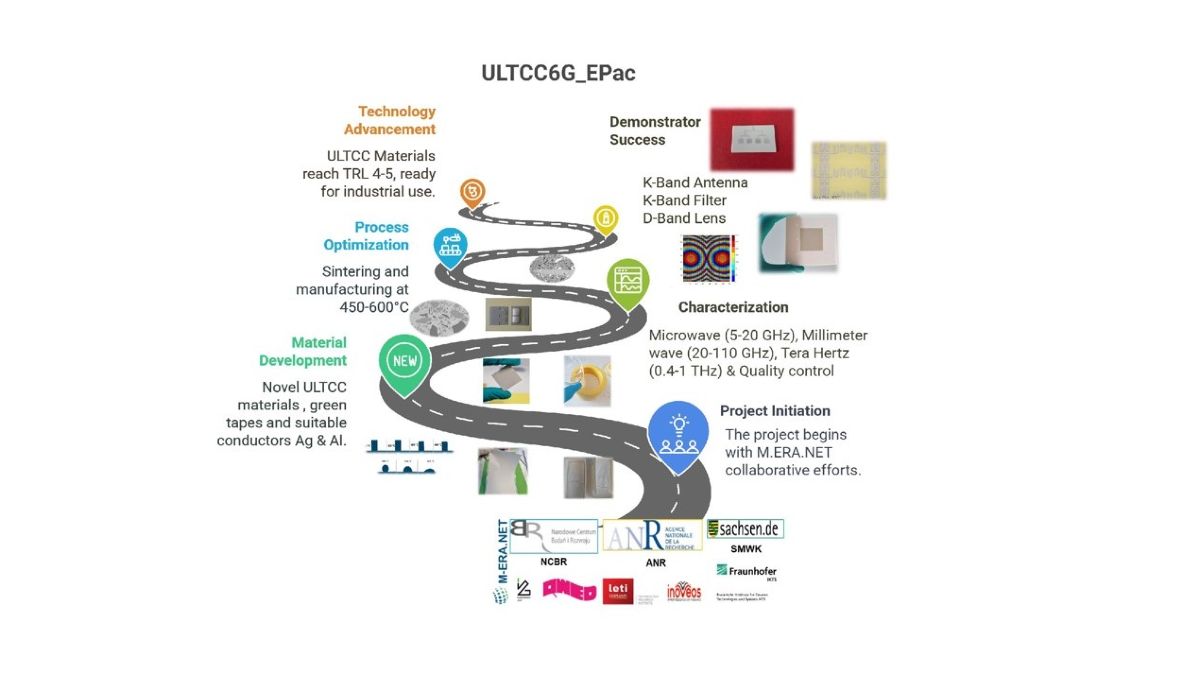
Multifunctional materials
ULTCC6G_EPac
The ULTCC6G_Epac project has achieved groundbreaking advancements in the development and validation of Ultra-Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (ULTCC) materials, paving the way for next-generation microwave and millimeter-wave applications. Through a collaborative effort involving leading research institutions and industry partners, the project has successfully progressed ULTCC materials to Technology Readiness Level 4-5, demonstrating their potential in real-world scenarios.
