Tellurium-Free Thermoelectric Modules by Interface Engineering - Thermos
Project summary
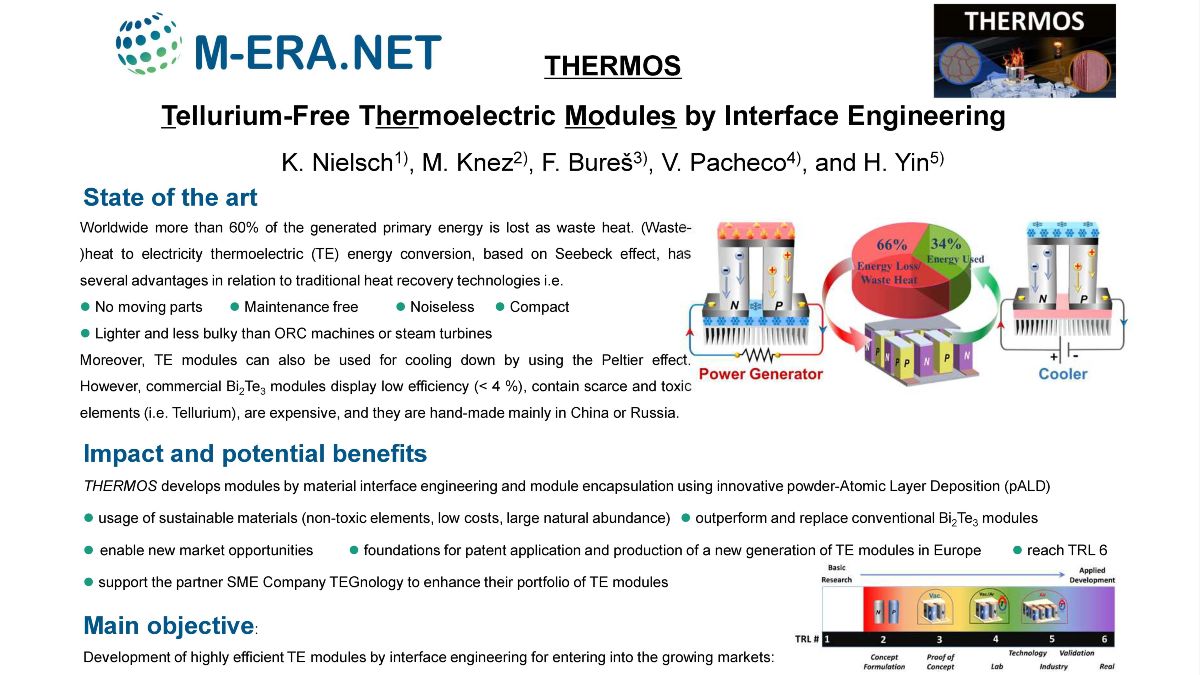
Thermoelectric (TE) technology offers solutions to solid-state heat recovery and cooling. Till now, only Bi2Te3 modules are commercially mature. Their applicability is limited by the scarcity and toxicity of tellurium (Te) with a concentration of <0.001 ppm in the earth’s crust. The replacement of Te will be addressed by THERMOS. As major objective THERMOS will develop highly efficient modules using atomic layer deposition and Te-free Zintl materials with a conversion efficiency of 8.5% and a cooling temperature of 65˚C to outperform Bi2Te3 modules. THERMOS will enable novel applications such as powering off-grid Internet-of-Things (IoT) nodes, energy harvesting from low-grade waste heat or cooling of medical devices. Joint efforts of research institutes from Germany and Spain, one university from the Czech Republic, and the Danish company TEGnology will impact the development and production of next-generation TE modules “Made in Europe” with better sustainability and performance.Project Details
Call
Call 2021
Call Topic
Functional materials
Project start
01.07.2022
Project end
30.06.2025
Total project costs
1.371.590 €
Total project funding
1.205.257 €
TRL
2 - 6
Coordinator
Prof. Dr. Kornelius Nielsch
k.nielsch@ifw-dresden.de
IFW Dresden, HELMHOLTZSTRASSE 20, 01069 DRESDEN, Germany
Partners and Funders Details
| Consortium Partner | Country | Funder | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFW Dresden https://www.ifw-dresden.de |
Research org. | Germany | DE-SMWK |
| CIC nanoGUNE https://www.nanogune.eu |
Research org. | Spain | ES-AEI |
| University of Pardubice https://www.upce.cz |
University | Czech Republic | CZ-TACR |
| Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM Dresden https://www.ifam-dd.fraunhofer.de |
Research org. | Germany | DE-SMWK |
| TEGnology ApS https://www.TEGnology.dk |
SME | Denmark | DK-IFD |
Keywords
thermoelectric materials, thermoelectric power generation, nanostructured materials, atomic layer deposition, sustainable energy source, Zintl Phase Materials, Topological Insulator